Error handling for remote module rendering in Module Federation.
Version Requirements
This solution requires upgrading the @module-federation/runtime version to 0.8.10 or higher.
Background
Remote module loading process may fail due to network resource loading failure or business logic rendering failure.
Though Module Federation Runtime provides detailed error log information and runtime hook to help users locate the cause of loading failure, we need to add error fallback mechanism to ensure the stability of the entire site, preventing the entire site from crashing due to the failure of a remote module rendering.
Solution
To build a robust remote module loading mechanism, we can handle possible problems from the following three levels:
The following solutions can refer to the examples in router-demo.
Network layer: Retry mechanism
Use @module-federation/retry-plugin plugin to handle network related issues:
-
Automatically retry failed resource requests
-
Configurable retry times and interval
-
Support custom error handling strategy
Loading layer: Error handling hook
Use Module Federation Runtime provided errorLoadRemote hook for more granular error handling:
- Capture errors in different loading lifecycle
- Provide fallback component or backup resource
- Support custom error handling strategy
Rendering layer: Error boundary
Use React's ErrorBoundary mechanism to handle component rendering exceptions:
- Graceful degradation, display friendly error prompts
- Isolate error impact, prevent the entire application from crashing
- Support error recovery and retry loading
These three solutions are for different scenarios, can be used separately, or combined to provide a more comprehensive error handling mechanism. Below we will introduce the specific implementation of each solution in detail.
Add retry mechanism
For weak network environment or producer has not started the service, we can add retry mechanism to request resources multiple times, which will increase the probability of resource loading success.
Module Federation official provides retry plugin @module-federation/retry-plugin to support retry mechanism for resources, support fetch and script resources retry.
Pure runtime registration
import React from 'react';
import { createInstance, loadRemote } from '@module-federation/enhanced/runtime';
import { RetryPlugin } from '@module-federation/retry-plugin';
const mf = createInstance({
name: 'host',
remotes: [
{
name: "remote1",
alias: "remote1"
entry: "http://localhost:2001/mf-manifest.json",
}
],
plugins: [
RetryPlugin({
retryTimes: 3,
retryDelay: 1000,
manifestDomains: ['https://domain1.example.com', 'https://domain2.example.com'],
domains: ['https://cdn1.example.com', 'https://cdn2.example.com'],
addQuery: ({ times, originalQuery }) => `${originalQuery}&retry=${times}`,
onRetry: ({ times, url }) => console.log('retry', times, url),
onSuccess: ({ url }) => console.log('success', url),
onError: ({ url }) => console.log('error', url),
}),
]
});
// Module loading
const Remote1Button = React.lazy(() => mf.loadRemote('remote1/button'));
export default () => {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div> Loading Remote1App...</div>}>
<Remote1Button />
</React.Suspense>
);
}
// Method/function loading
mf.loadRemote<{add: (...args: Array<number>)=> number }>("remote1/util").then((md)=>{
md.add(1,2,3);
});
More about the parameter configuration of @module-federation/retry-plugin please see document
Plugin registration
import { pluginModuleFederation } from '@module-federation/rsbuild-plugin';
import { defineConfig } from '@rsbuild/core';
import { pluginReact } from '@rsbuild/plugin-react';
import path from 'path';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
pluginReact(),
pluginModuleFederation({
name: 'host',
runtimePlugins: [
path.join(__dirname, './src/runtime-plugin/retry.ts'),
],
}),
],
});
// src/runtime-plugin/retry.ts
import { RetryPlugin } from '@module-federation/retry-plugin';
const retryPlugin = () =>
RetryPlugin({
retryTimes: 3,
retryDelay: 1000,
manifestDomains: ['https://domain1.example.com', 'https://domain2.example.com'],
domains: ['https://cdn1.example.com', 'https://cdn2.example.com'],
addQuery: ({ times, originalQuery }) => `${originalQuery}&retry=${times}`,
onRetry: ({ times, url }) => console.log('retry', times, url),
onSuccess: ({ url }) => console.log('success', url),
onError: ({ url }) => console.log('error', url),
});
export default retryPlugin;
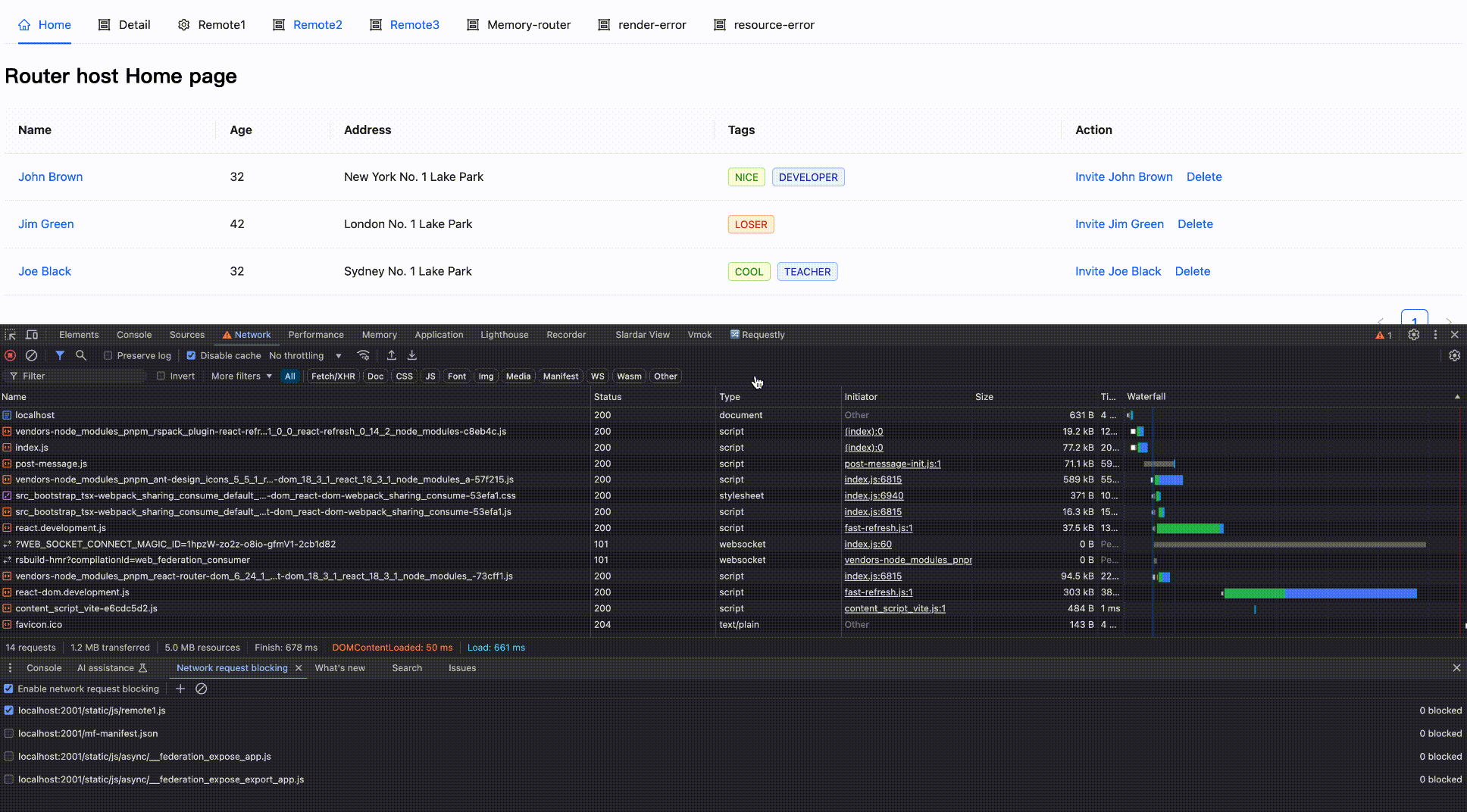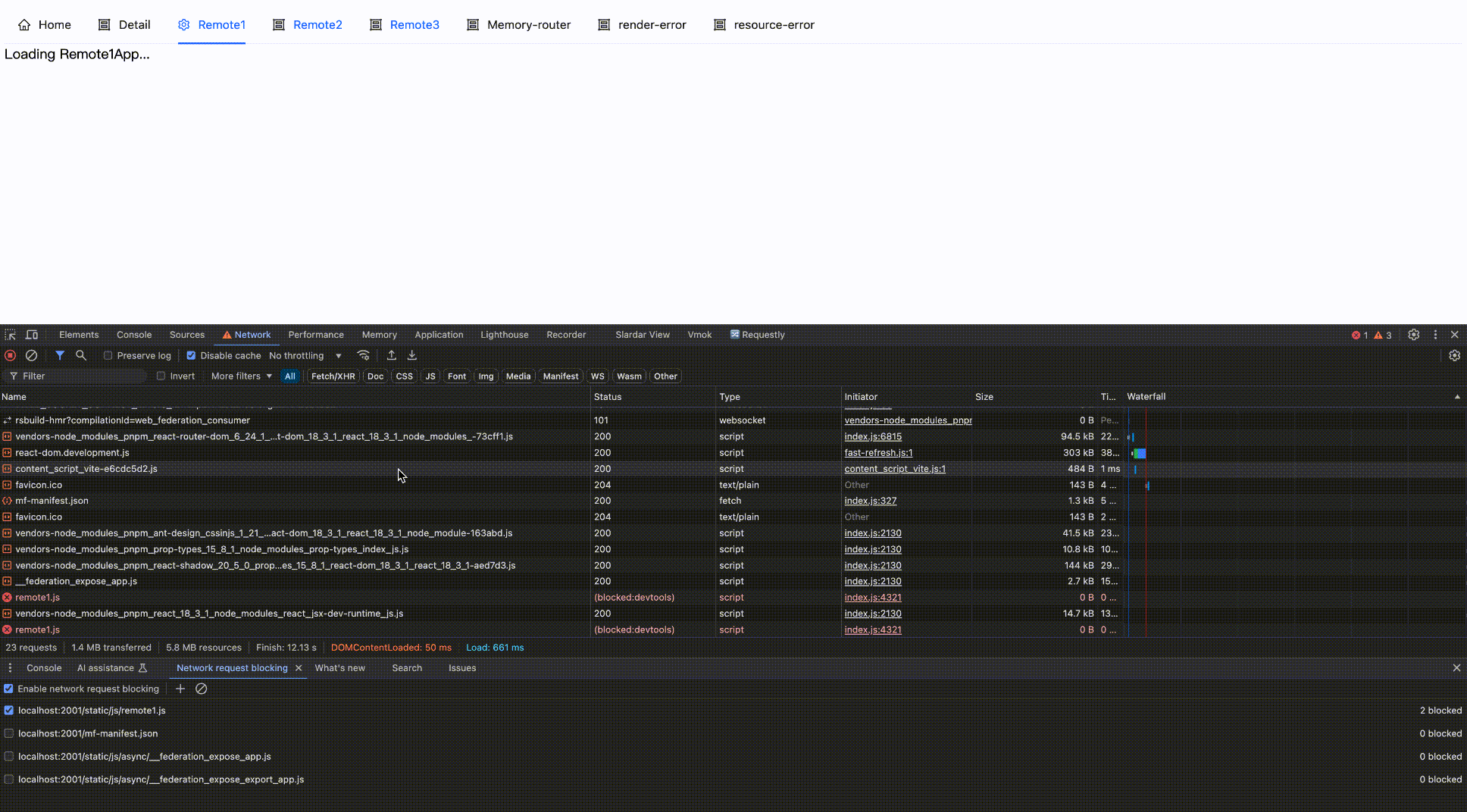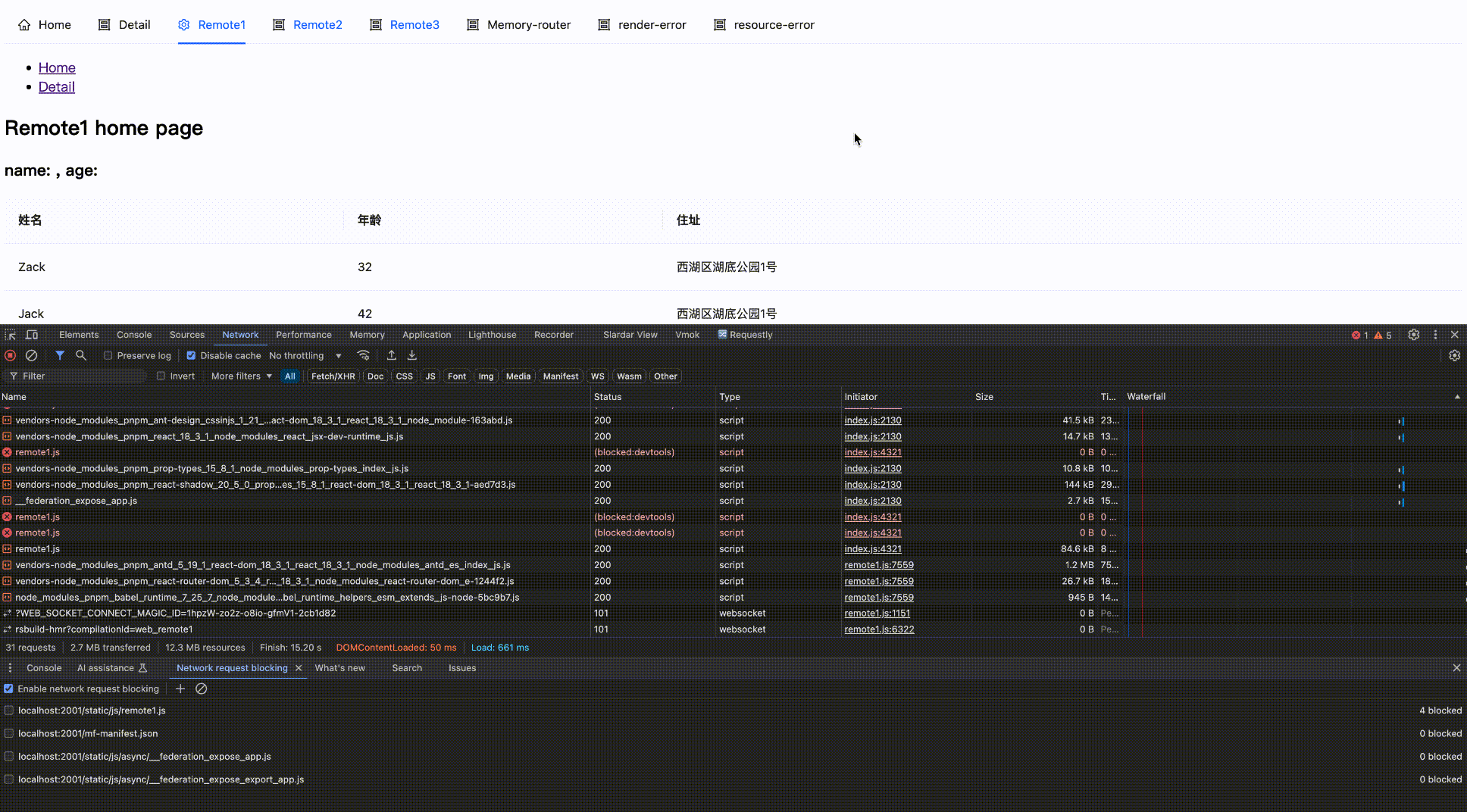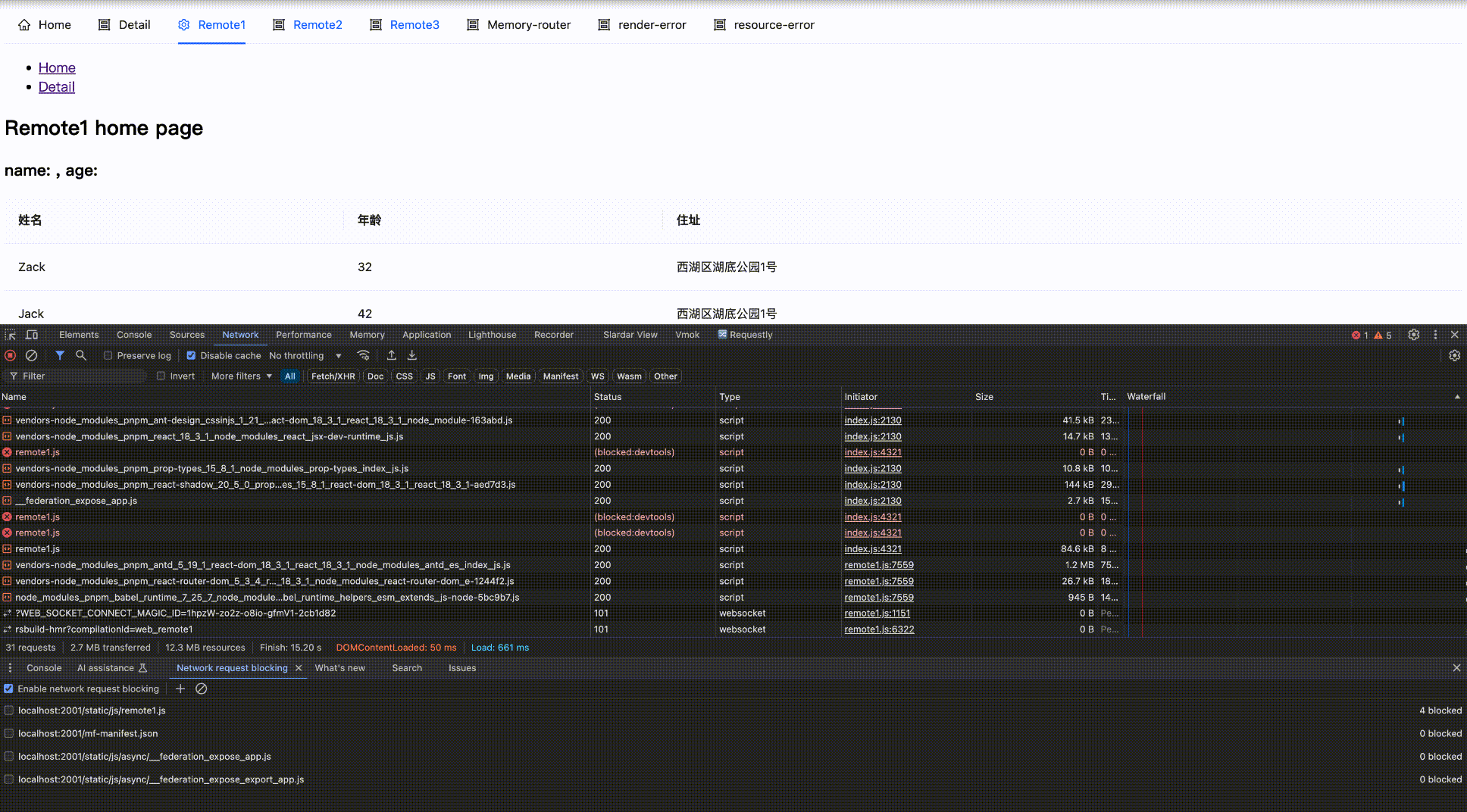
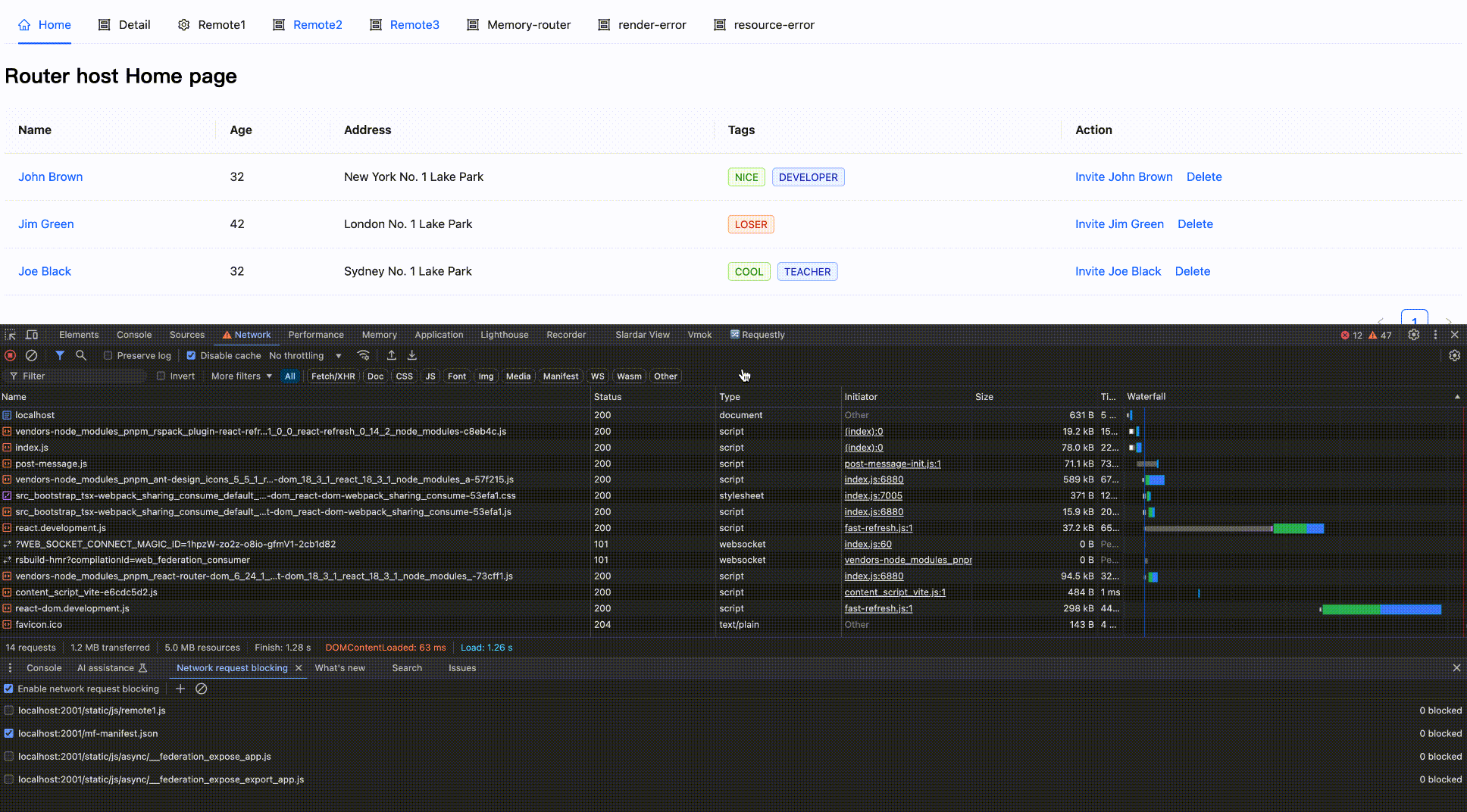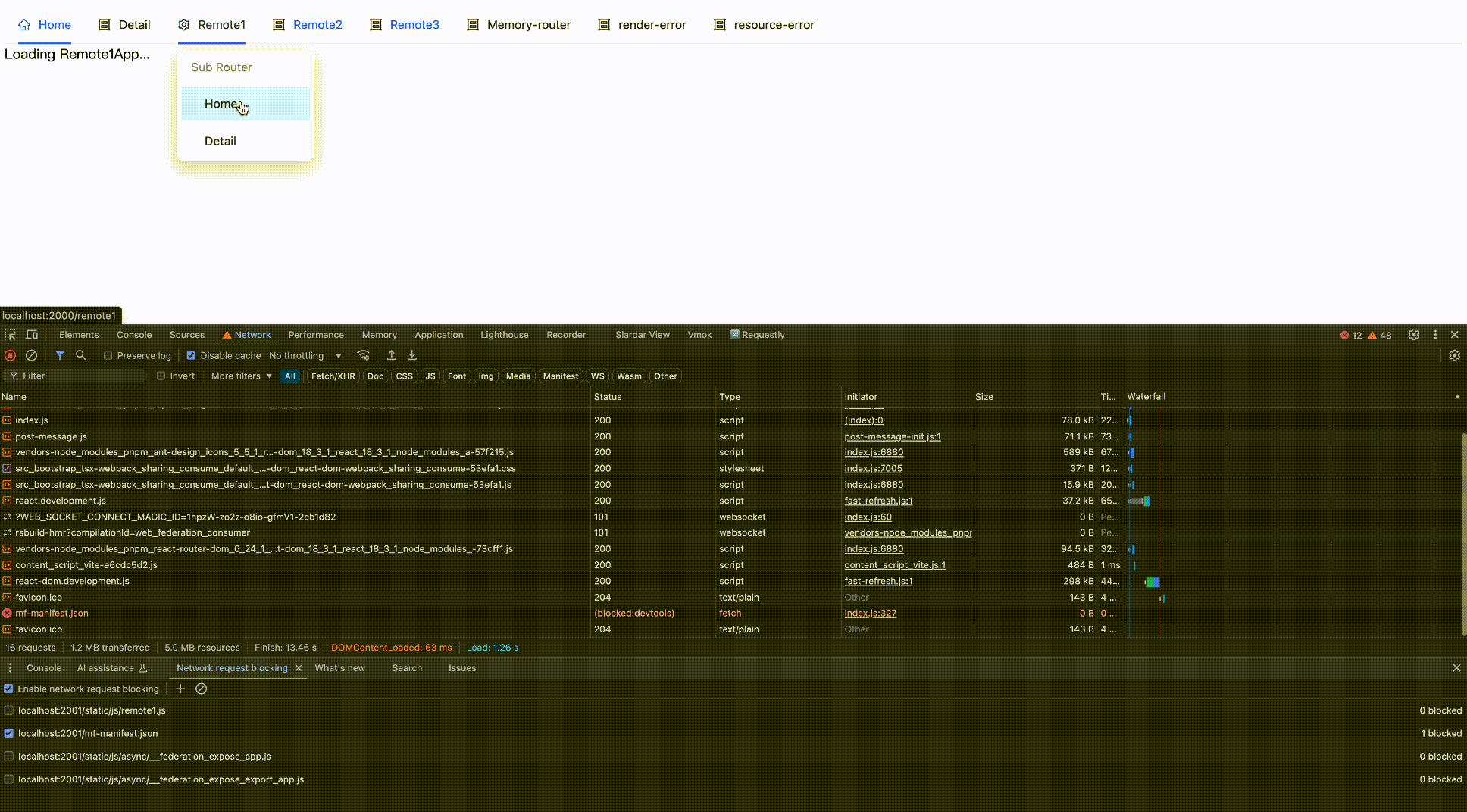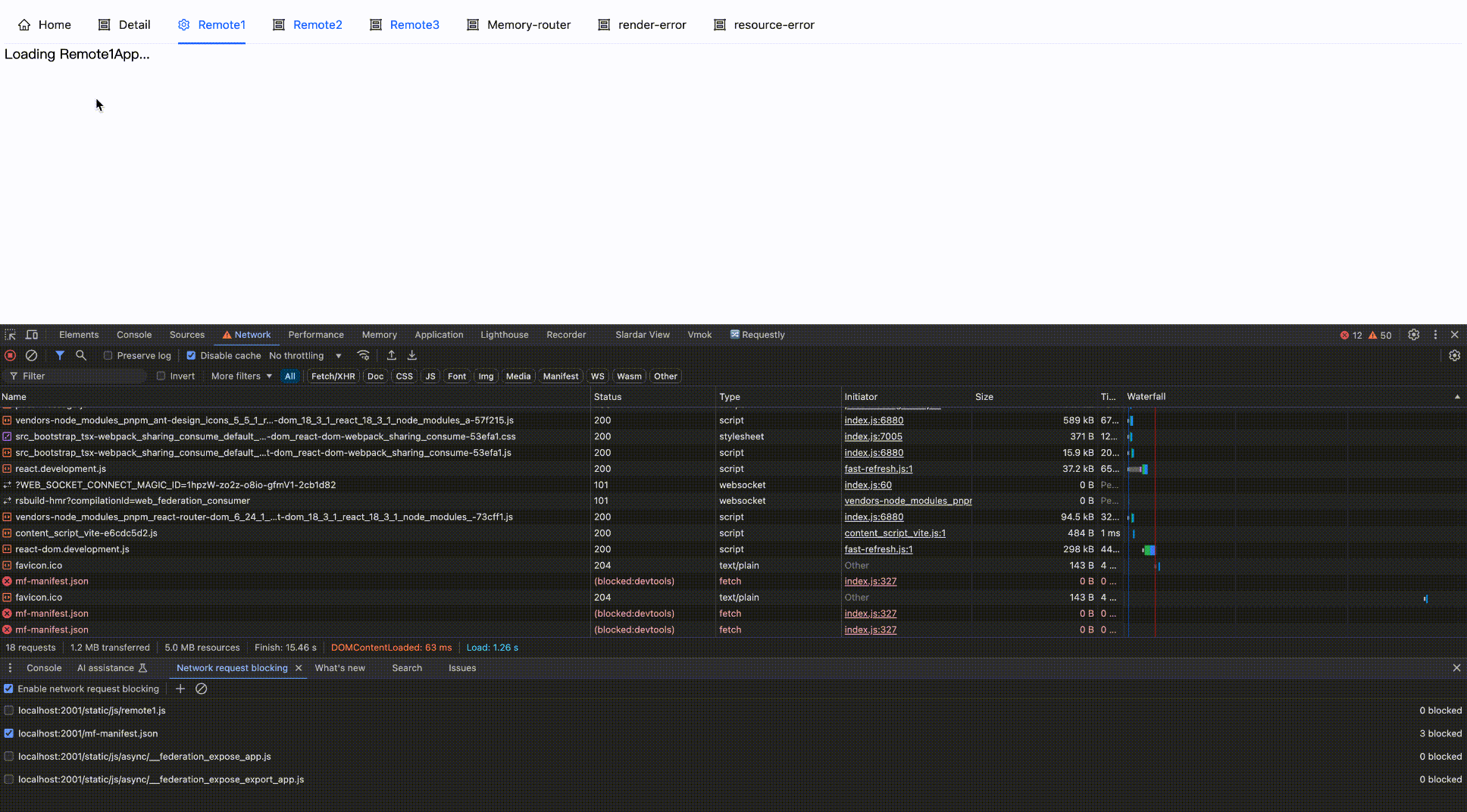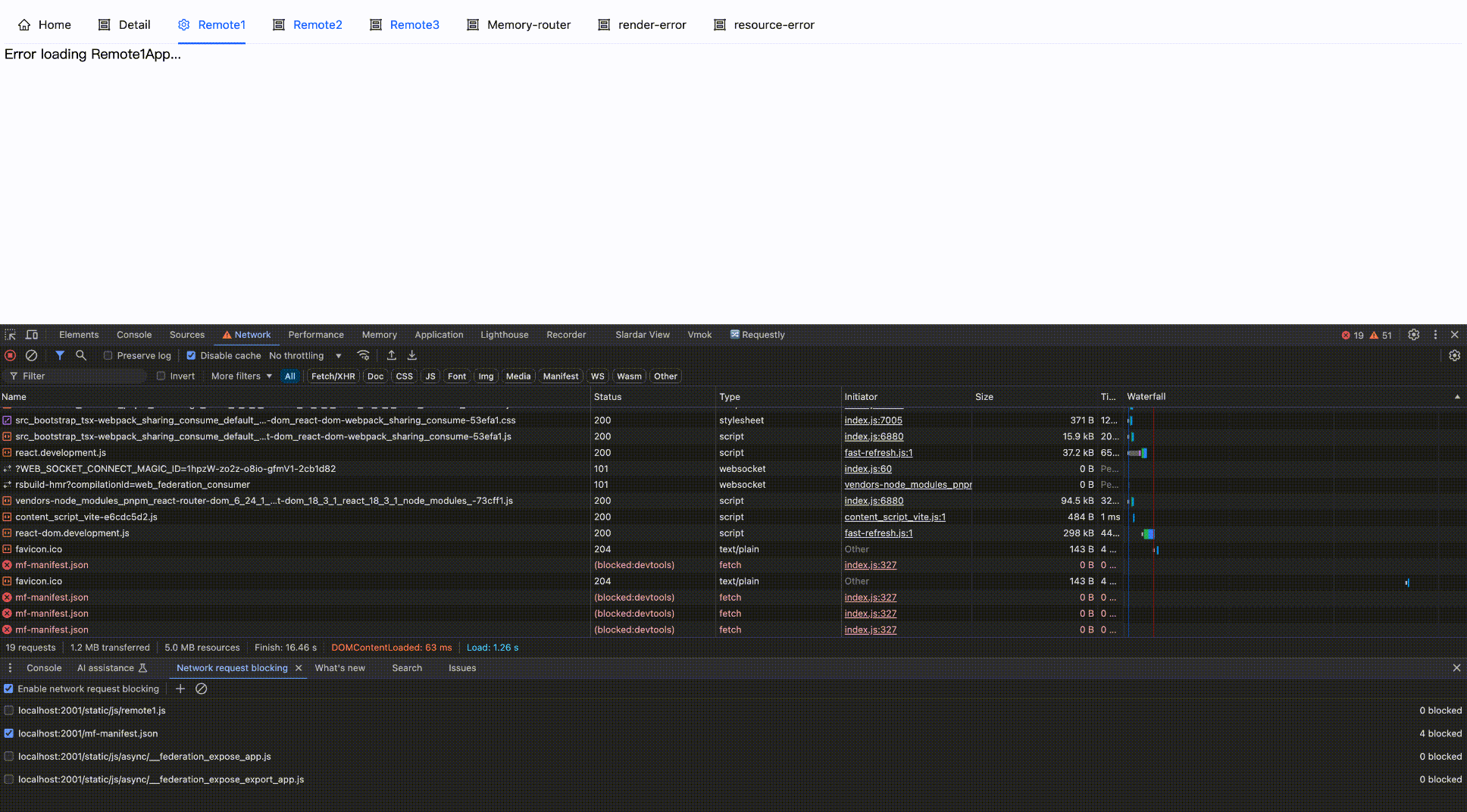
Effect as follows:
Block network request
Block then Enable
errorLoadRemote hook
For errors in the loading process of remote modules, they can be captured in the errorLoadRemote hook.
errorLoadRemote is the hook for error handling in Module Federation Runtime. When the remote module loading fails, this hook will be triggered. It is designed to trigger when the module loading fails in different lifecycle stages, and allow users to customize error handling strategies.
errorLoadRemote supports returning a fallback component for error fallback, and also supports returning specific resource content to ensure subsequent processes render normally.
We divide the usage of module registration and loading into "pure runtime + dynamic import" and "plugin registration + synchronous import".
Pure runtime + dynamic import
When using pure runtime registration, the remote module will not request resources until after registration.
import React from 'react';
import { createInstance, loadRemote } from '@module-federation/enhanced/runtime';
import { RetryPlugin } from '@module-federation/retry-plugin';
// Module registration
const mf = createInstance({
name: 'host',
remotes: [
{
name: "remote1",
entry: "http://localhost:2001/mf-manifest.json",
alias: "remote1"
}
],
plugins: [
RetryPlugin({
retryTimes: 3,
retryDelay: 1000,
}),
]
});
// Module loading
const Remote1Button = React.lazy(() => loadRemote('remote1/button'));
export default () => {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div> Loading Remote1App...</div>}>
<Remote1Button />
</React.Suspense>
);
}
// Method/function loading
loadRemote<{add: (...args: Array<number>)=> number }>("remote1/util").then((md)=>{
md.add(1,2,3);
});
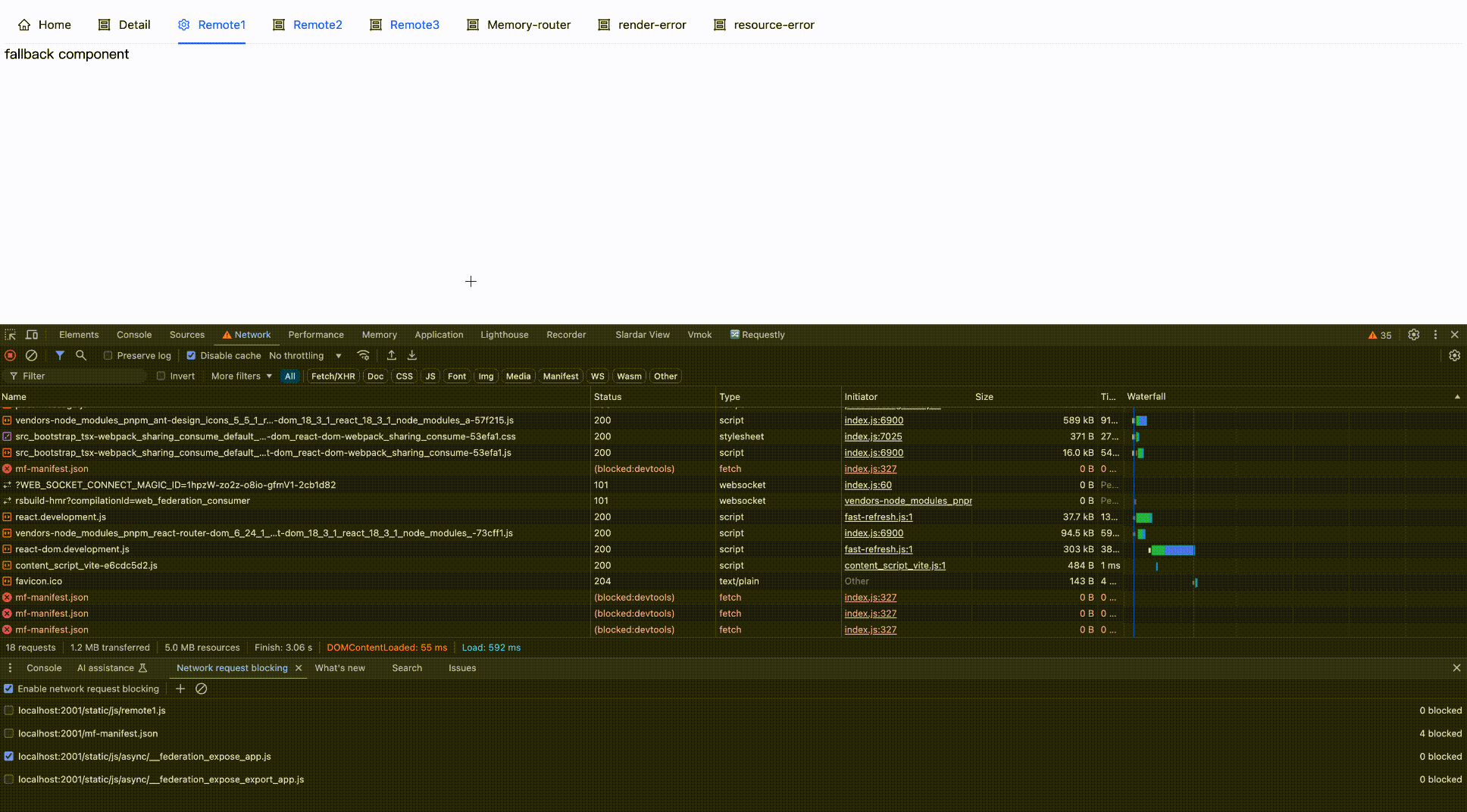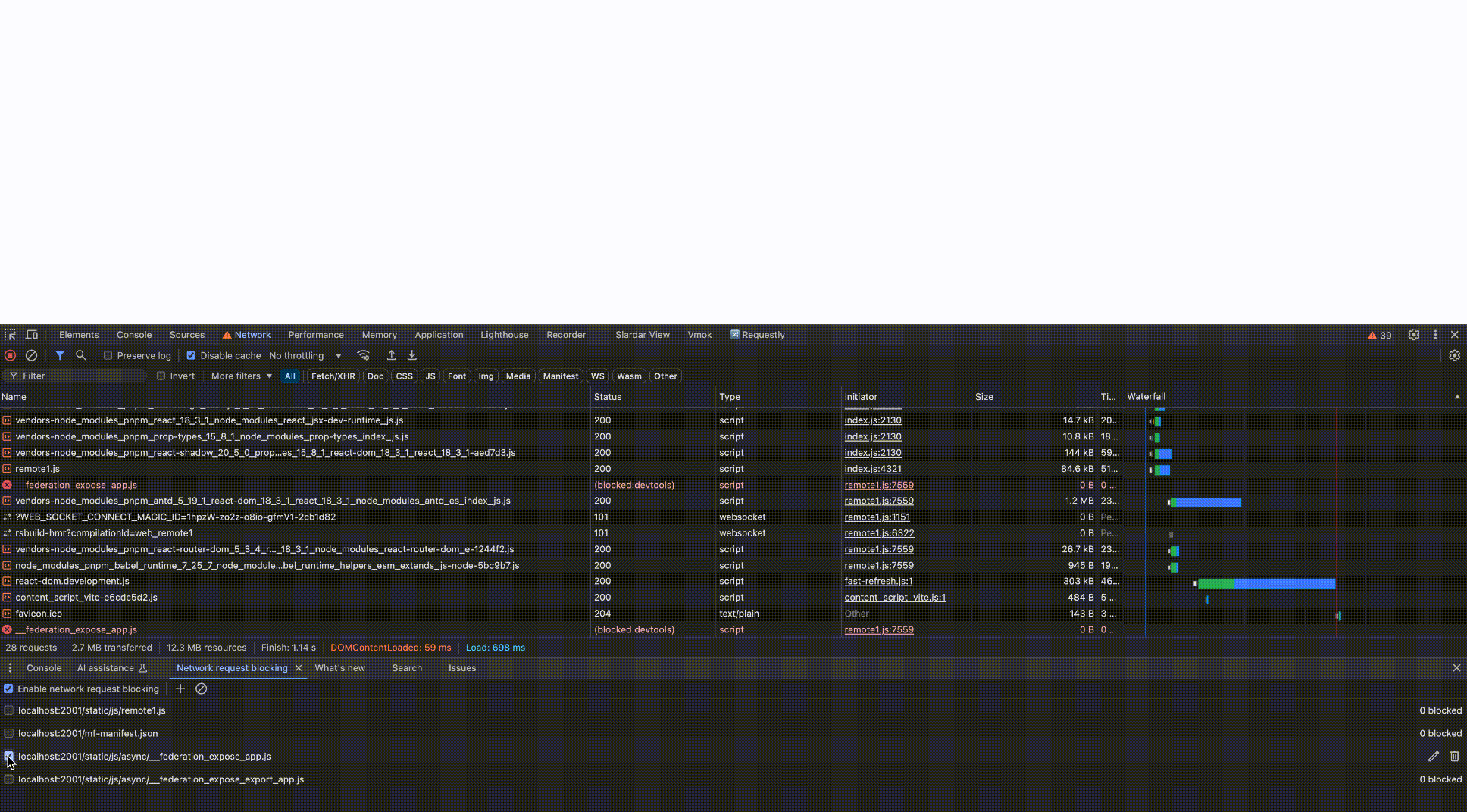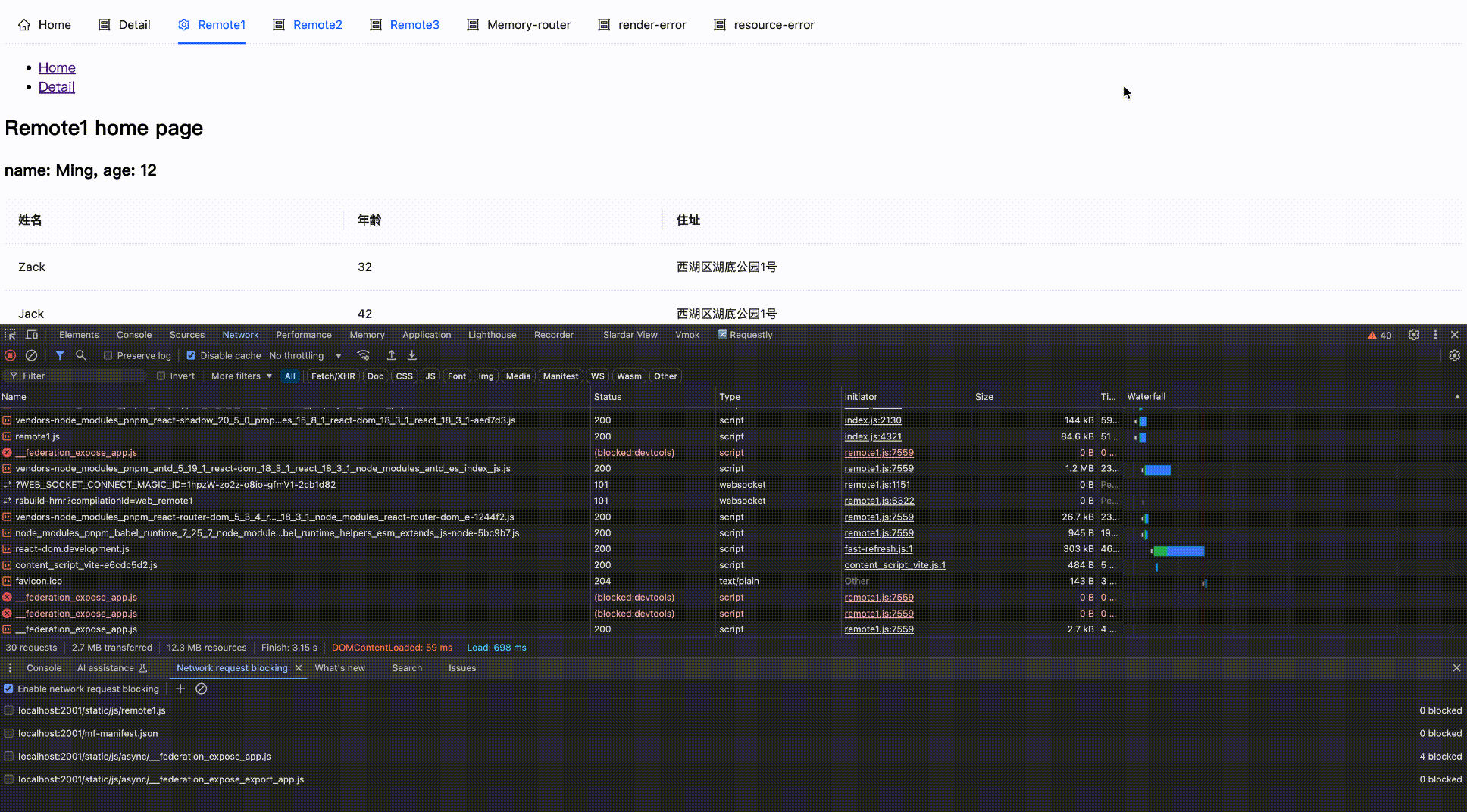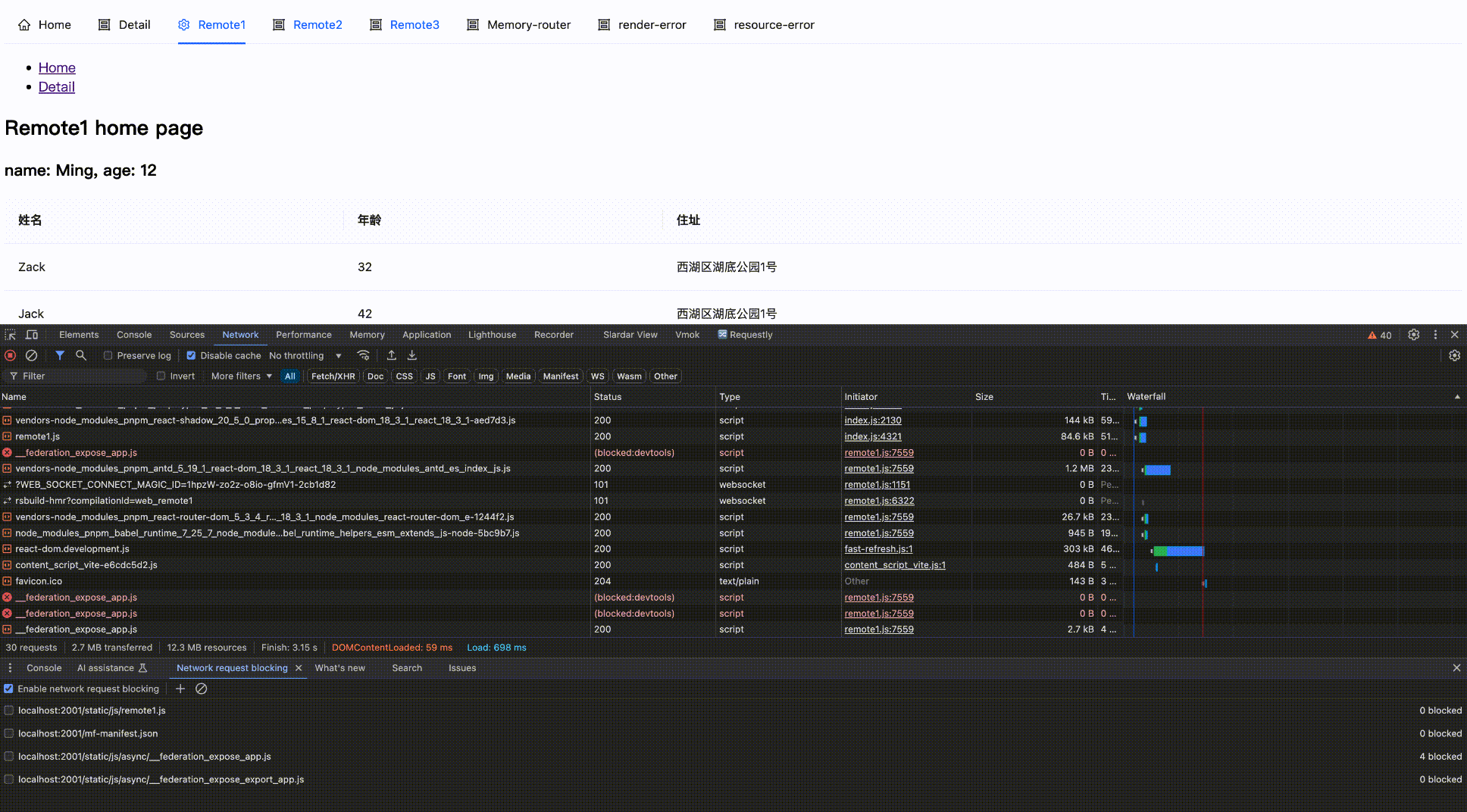
Use the errorLoadRemote hook to capture remote module loading errors (including resource loading errors), and support returning errorBoundary fallback component.
import React from 'react';
import { createInstance, loadRemote } from '@module-federation/enhanced/runtime';
import { RetryPlugin } from '@module-federation/retry-plugin';
const fallbackPlugin: () => ModuleFederationRuntimePlugin = function () {
return {
name: 'fallback-plugin',
errorLoadRemote(args) {
return { default: () => <div> fallback component </div> };
},
};
};
// Module registration
const mf = createInstance({
name: 'host',
remotes: [
{
name: "remote1",
alias: "remote1"
entry: "http://localhost:2001/mf-manifest.json",
}
],
plugins: [
RetryPlugin({
retryTimes: 3,
retryDelay: 1000,
}),
fallbackPlugin()
]
});
// Module loading
const Remote1Button = React.lazy(() => mf.loadRemote('remote1/button'));
export default () => {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div> Loading Remote1App...</div>}>
<Remote1Button />
</React.Suspense>
);
}
// Method/function loading
mf.loadRemote<{add: (...args: Array<number>)=> number }>("remote1/util").then((md)=>{
md.add(1,2,3);
});
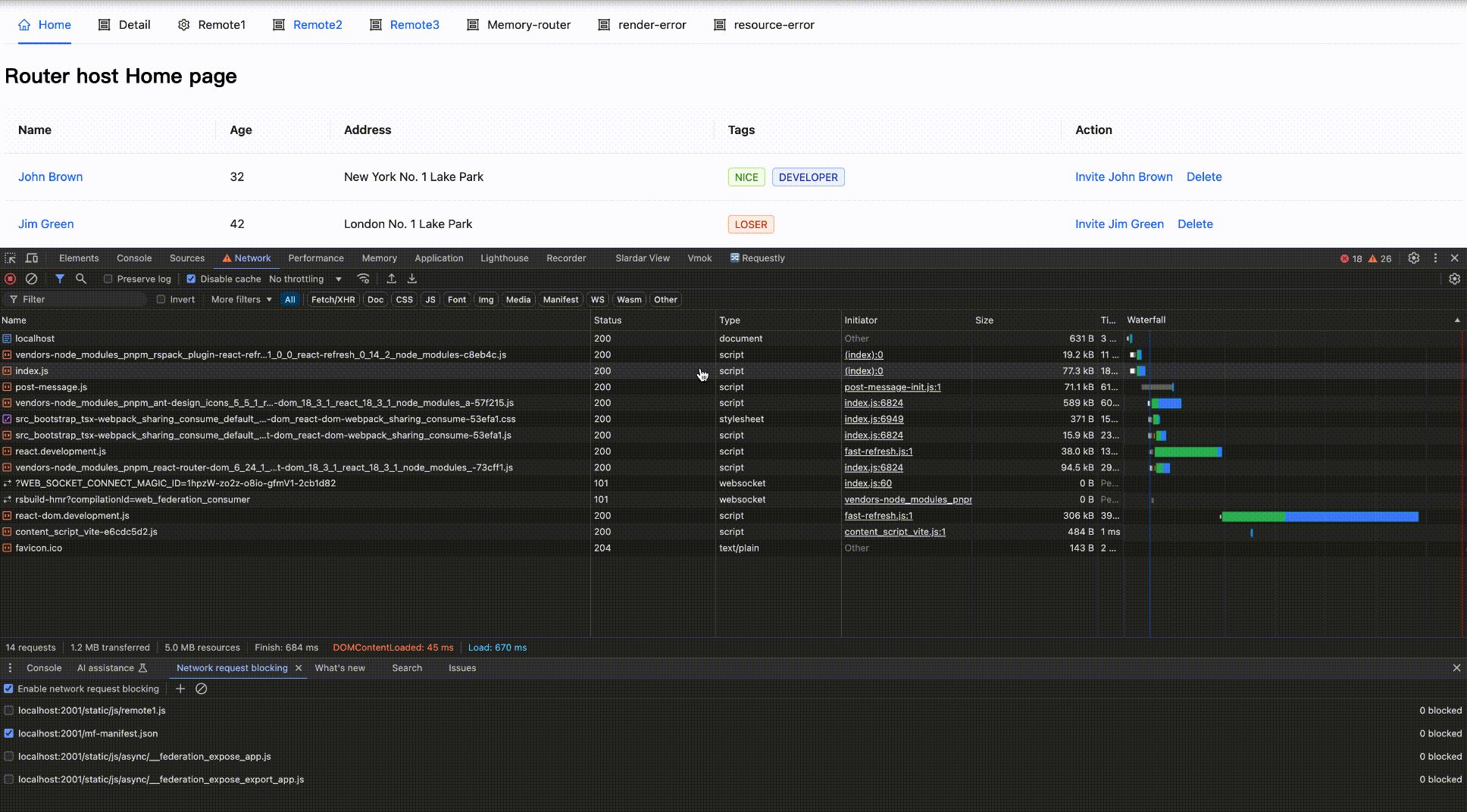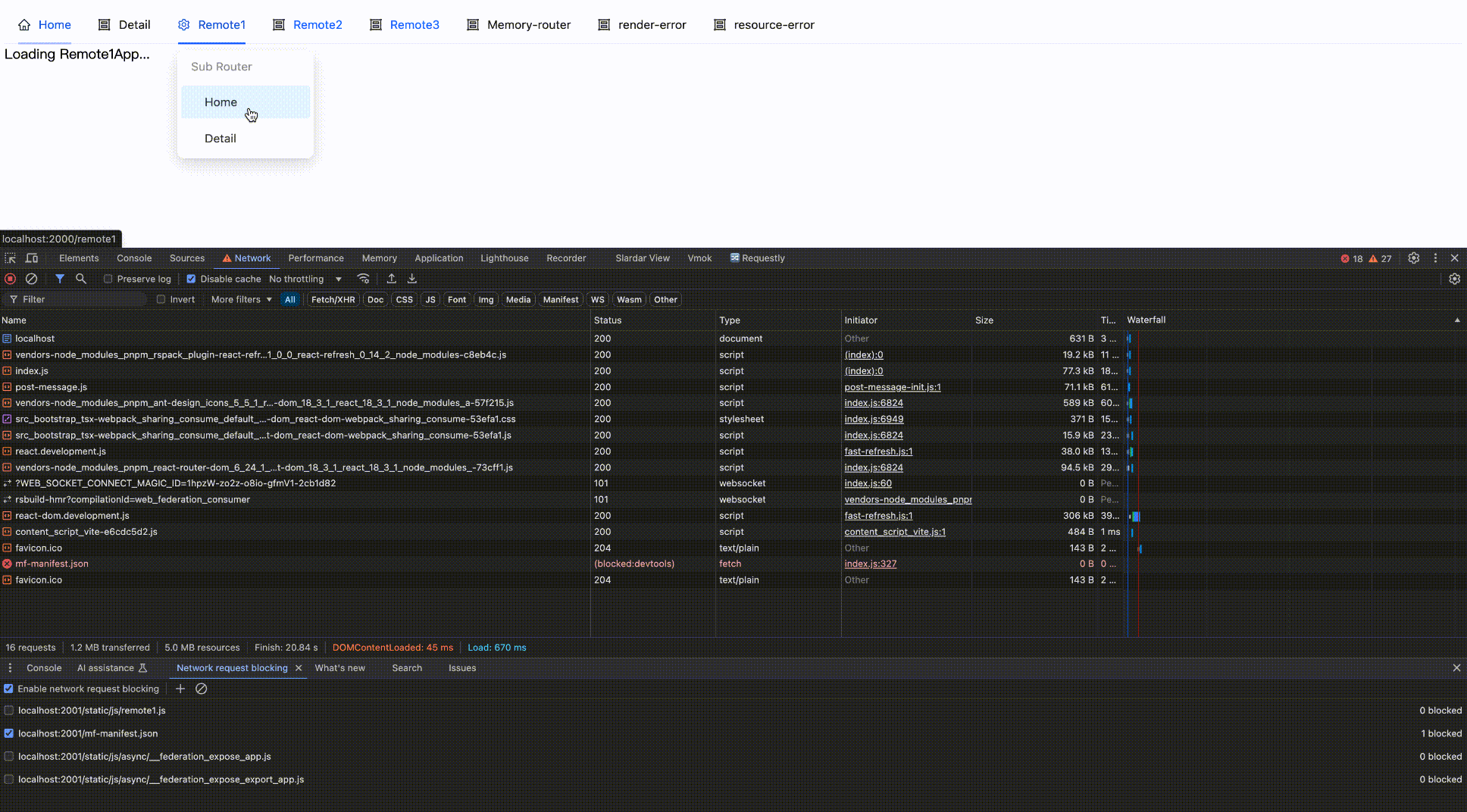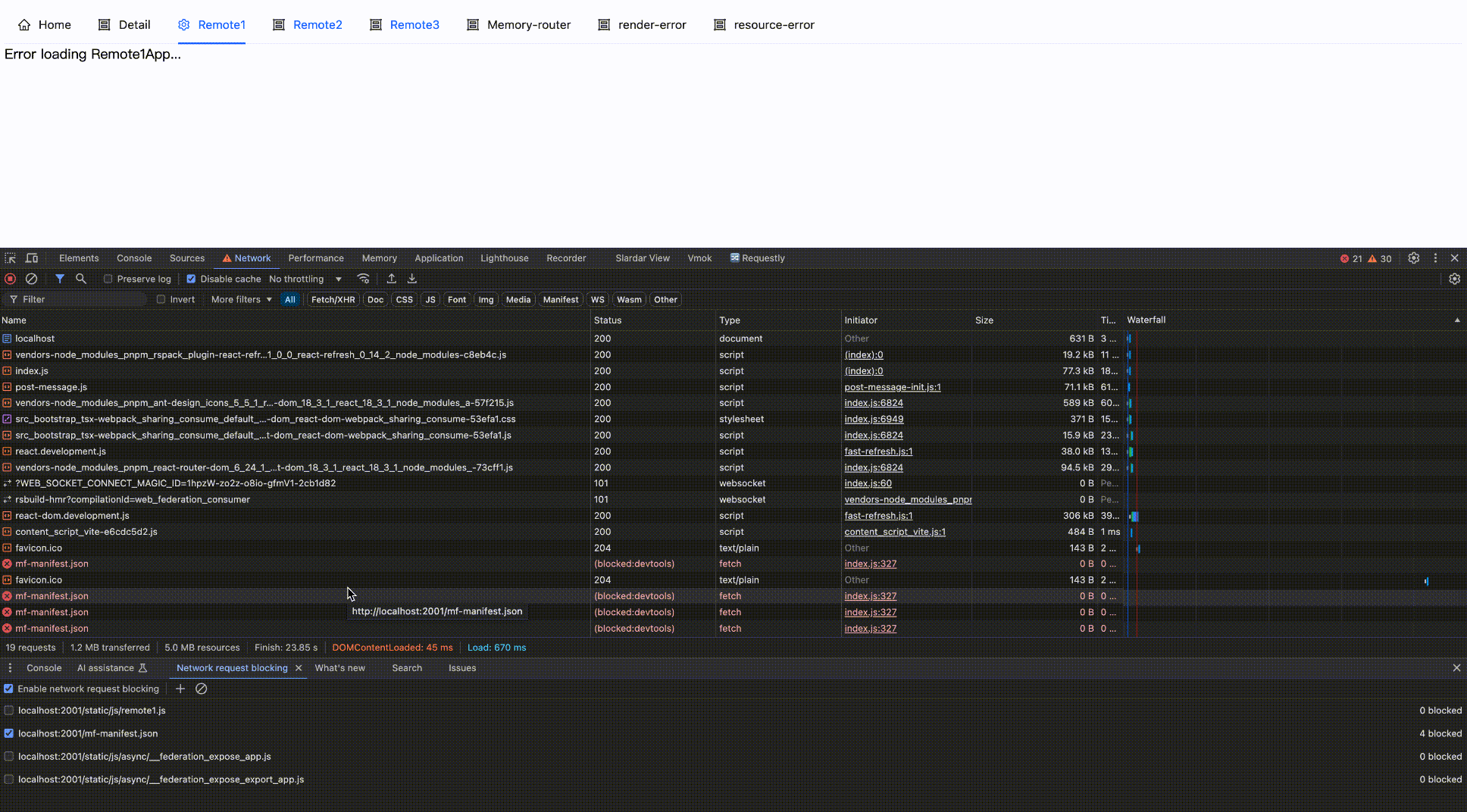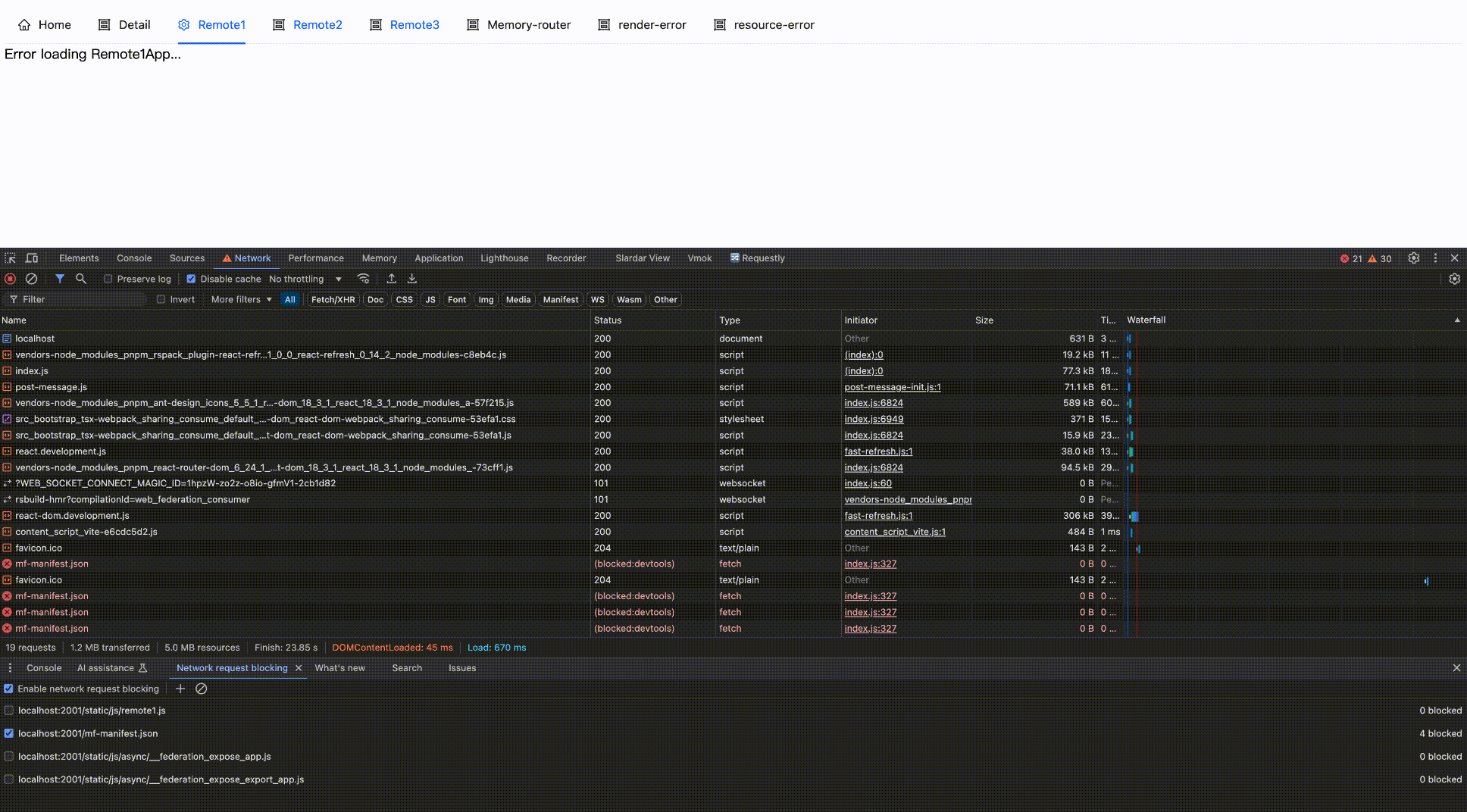
Effect as follows:
Block network request
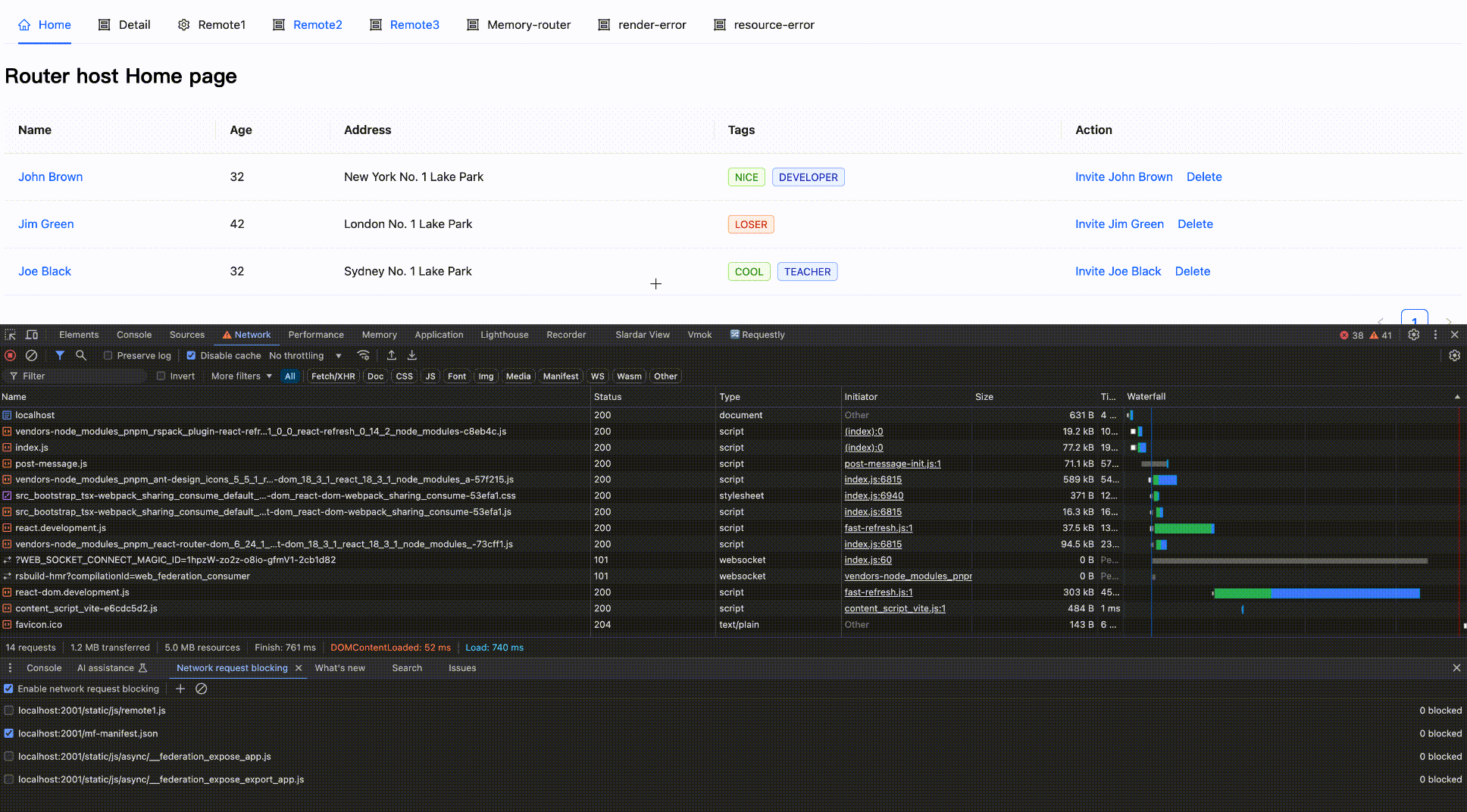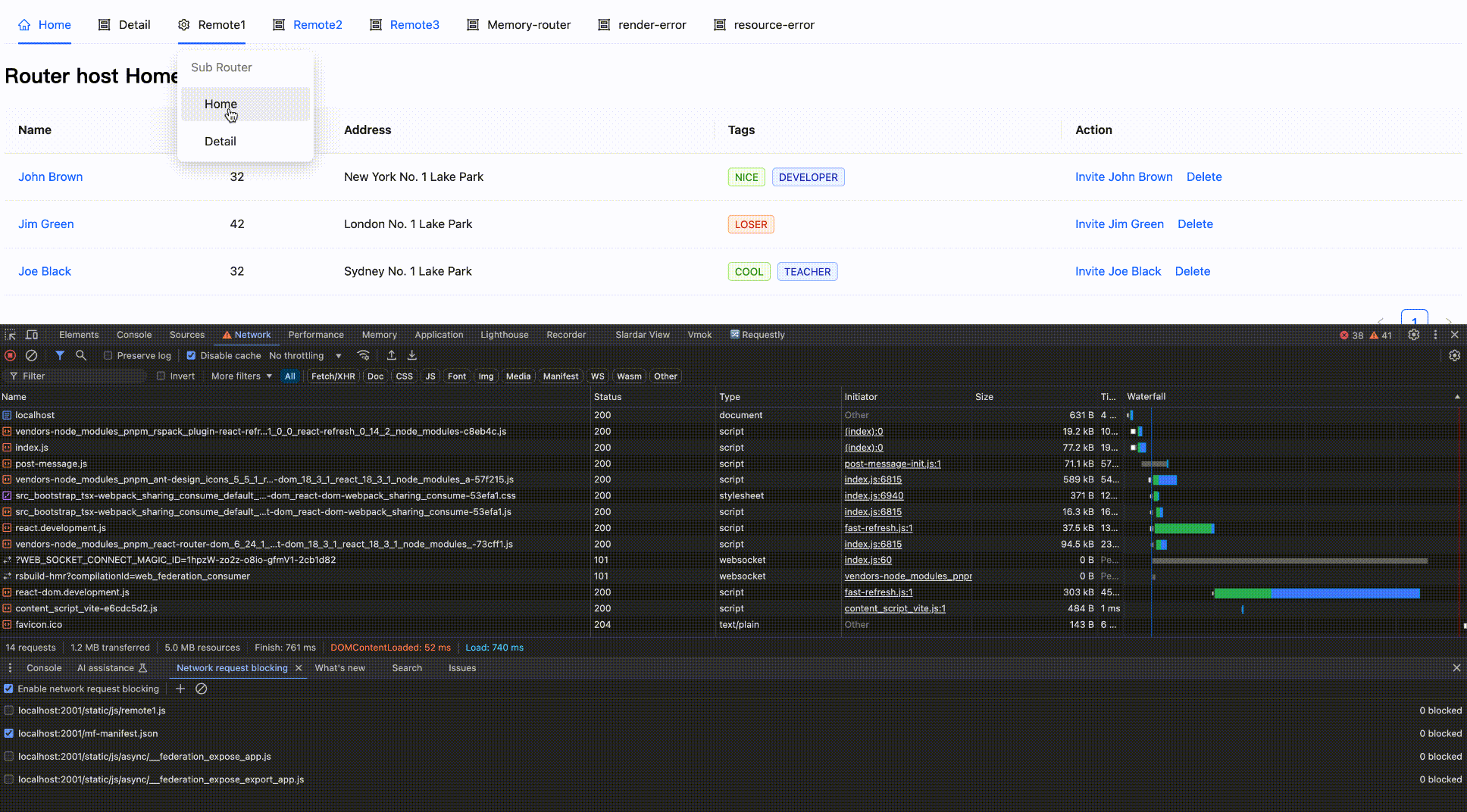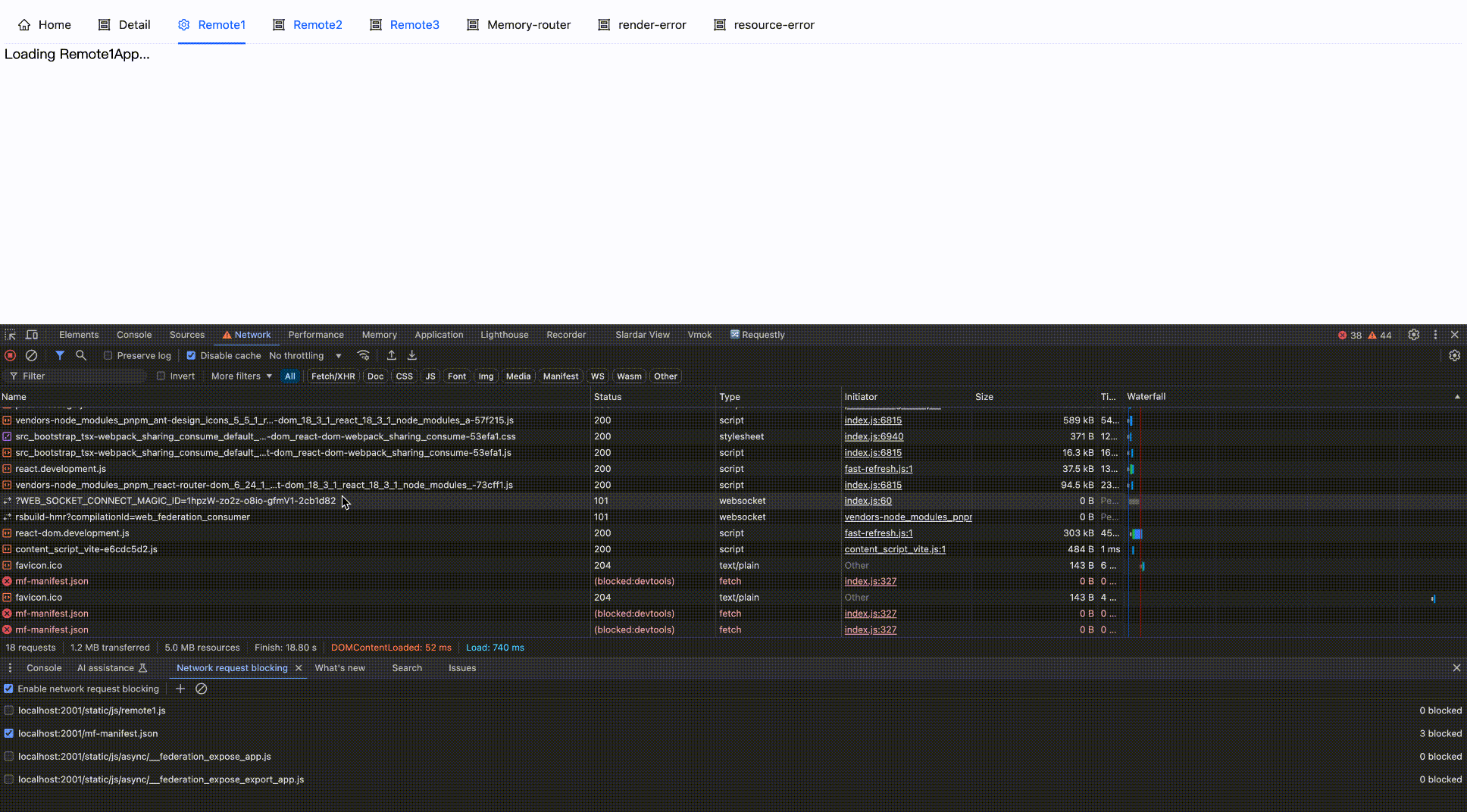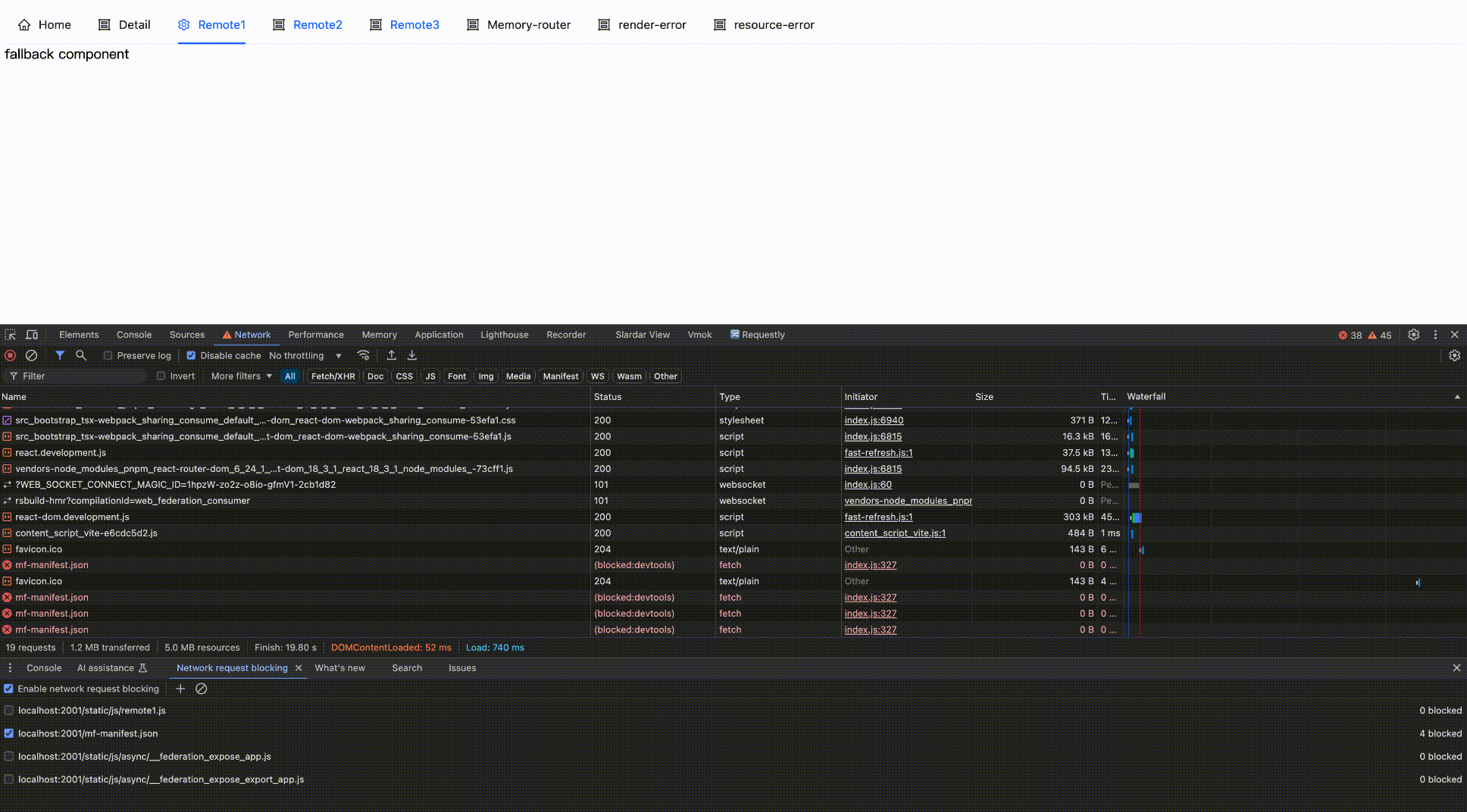
Block then Enable
Plugin registration + synchronous import
Plugin registration supports using synchronous import to load modules, and the resource request timing is earlier than pure runtime, so we need to register the errorLoadRemote hook in the plugin.
// rsbuild.config.ts
import { pluginModuleFederation } from '@module-federation/rsbuild-plugin';
import { defineConfig } from '@rsbuild/core';
import { pluginReact } from '@rsbuild/plugin-react';
import path from 'path';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
pluginReact(),
pluginModuleFederation({
name: 'host',
remotes: {
remote1: 'remote1@http://localhost:2001/mf-manifest.json',
},
runtimePlugins: [
path.join(__dirname, './src/runtime-plugin/retry.ts'),
path.join(__dirname, './src/runtime-plugin/fallback.ts'),
],
...
}),
],
});
Tips
The following example shows how to handle errors in different lifecycle stages.
If your application scenario is simple, you can refer to the simplified version below, which provides a unified error handling solution.
// src/runtime-plugin/fallback.ts
import type { ModuleFederationRuntimePlugin } from '@module-federation/runtime';
interface FallbackConfig {
// Backup service address
backupEntryUrl?: string;
// Custom error message
errorMessage?: string;
}
const fallbackPlugin = (config: FallbackConfig = {}): ModuleFederationRuntimePlugin => {
const {
backupEntryUrl = 'http://localhost:2002/mf-manifest.json',
errorMessage = 'Module loading failed, please try again later'
} = config;
return {
name: 'fallback-plugin',
async errorLoadRemote(args) {
// Handle component loading errors
if (args.lifecycle === 'onLoad') {
const React = await import('react');
// Create a fallback component with error message
const FallbackComponent = React.memo(() => {
return React.createElement(
'div',
{
style: {
padding: '16px',
border: '1px solid #ffa39e',
borderRadius: '4px',
backgroundColor: '#fff1f0',
color: '#cf1322'
}
},
errorMessage
);
});
FallbackComponent.displayName = 'ErrorFallbackComponent';
return () => ({
__esModule: true,
default: FallbackComponent
});
}
// Handle entry file loading errors
if (args.lifecycle === 'afterResolve') {
try {
// Try to load backup service
const response = await fetch(backupEntryUrl);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Failed to fetch backup entry: ${response.statusText}`);
}
const backupManifest = await response.json();
console.info('Successfully loaded backup manifest');
return backupManifest;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to load backup manifest:', error);
// If backup service also fails, return original error
return args;
}
}
return args;
},
};
};
export default fallbackPlugin;
Effect as follows:
Block network request
Block then Enable
Set ErrorBoundary for component
React's ErrorBoundary is the last line of defense for handling component-level errors, in the dynamic loading scenario of remote modules (such as lazy loading), it can help us capture and process the rendering errors of remote modules and provide graceful degradation.
Setting ErrorBoundary for components is suitable for dynamic import remote module scenarios, such as lazy loading scenarios.
Moreover, after setting ErrorBoundary for components, you can avoid relying on the errorLoadRemote hook for error fallback, which is a feature of React itself to provide error fallback for your components.
App.tsx dynamic import remote module
// App.tsx
import React, {
useRef,
useEffect,
ForwardRefExoticComponent,
Suspense,
} from 'react';
const Remote1AppWithLoadRemote = React.lazy(() => loadRemote('remote1/app'));
const Remote1AppWithErrorBoundary = React.forwardRef<any, any>((props, ref) => (
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div>Error loading Remote1App...</div>}>
<Suspense fallback={<div> Loading Remote1App...</div>}>
<Remote1AppWithLoadRemote {...props} ref={ref} />
</Suspense>
</ErrorBoundary>
));
export default function App() {
return (
<>
<div className="flex flex-row">
<h2>Remote1</h2>
<Remote1AppWithErrorBoundary />
</div>
</>
);
}
Effect as follows:
Block network request
Block then Enable